The Dangers of Gallstones: How Your Diet Can Impact Gallstone Formation
- Abhilash Kumar
- May 30, 2024
- 2 min read
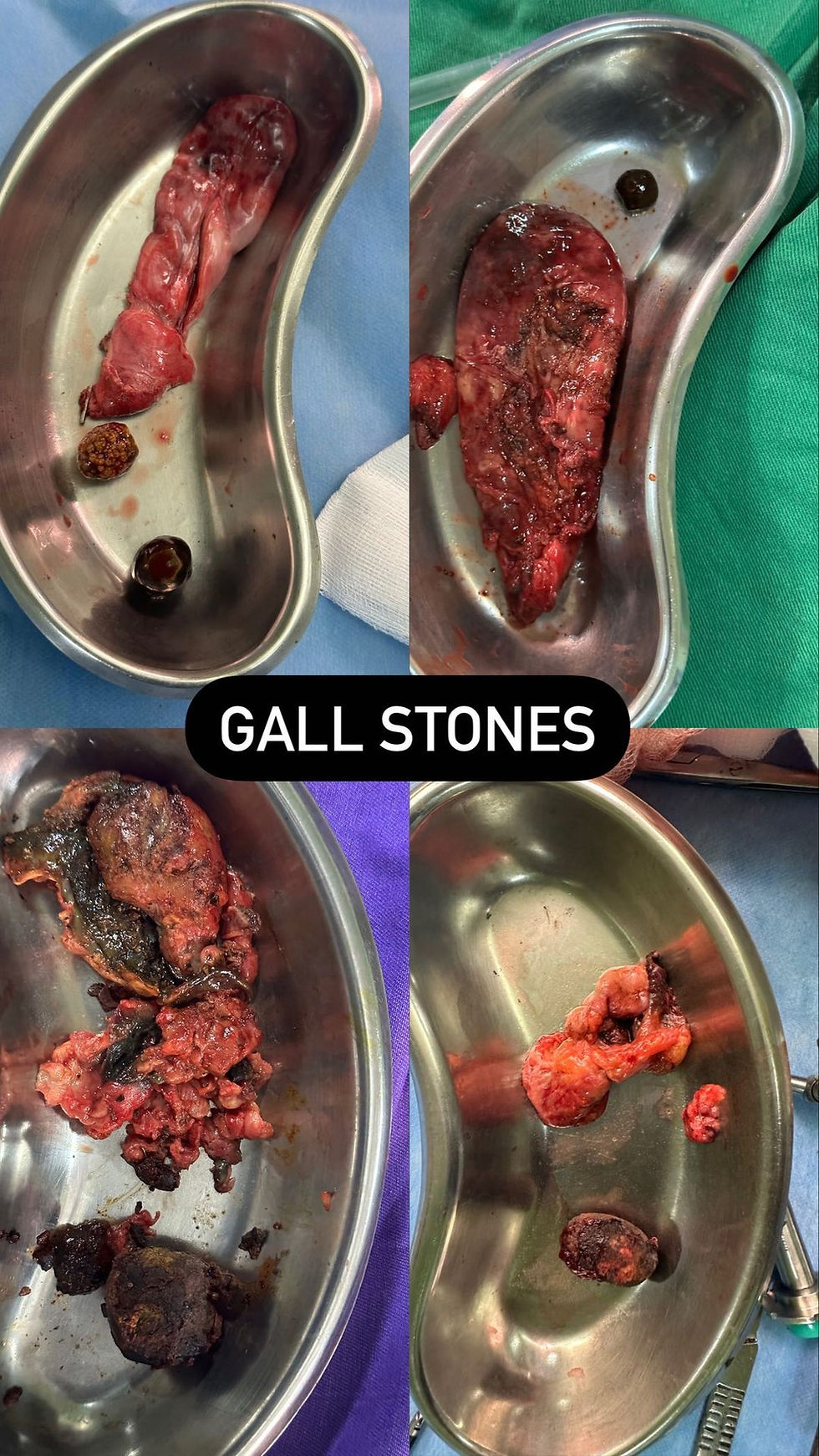
Certainly! Here’s an expanded version of the information on gallbladder stones, including details on complications:
Gallbladder Stones (Cholelithiasis): Symptoms, Investigations, Treatment, and Complications
Gallstones, or cholelithiasis, are solid deposits that form in the gallbladder. They can vary in size and composition, often consisting of cholesterol, bilirubin, and calcium salts. While some people remain asymptomatic, others experience discomfort and complications. Let’s delve deeper:
Symptoms:
Biliary Colic: The hallmark symptom is biliary colic—a sudden, intense pain in the upper right abdomen. This pain may radiate to the back or right shoulder.
Nausea and Vomiting: Gallstone attacks often cause nausea and vomiting.
Fever and Jaundice: In severe cases, gallstones can lead to inflammation (cholecystitis) or blockage of the bile ducts (choledocholithiasis), resulting in fever and jaundice.
Complications: If a gallstone obstructs the common bile duct, it can lead to pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas).
Investigations:
Abdominal Ultrasound: The primary diagnostic tool for detecting gallstones.
Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS): Useful for identifying smaller stones missed on regular ultrasound.
Other Imaging Tests: Oral cholecystography, HIDA scan, CT, MRCP, and ERCP provide additional information.
Blood Tests: Assess liver function, infection, and jaundice.
Treatment Options:
Asymptomatic Gallstones: If asymptomatic, no immediate treatment is necessary. Regular follow-up is essential.
Surgery (Cholecystectomy): Removal of the gallbladder is the definitive treatment for symptomatic gallstones. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is the preferred approach.
Medications: Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) can help dissolve cholesterol stones, but it’s a slow process.
Self-Care: Maintain a healthy weight, avoid fatty foods, and stay hydrated.
Specialists: Consult a gastroenterologist or general surgeon for personalized advice.
Complications:
Cholecystitis: Inflammation of the gallbladder due to gallstone obstruction.
Choledocholithiasis: Stones in the common bile duct can cause jaundice, pancreatitis, and cholangitis (bile duct infection).
Gallstone Ileus: Rarely, a large stone can obstruct the small intestine.
Gallbladder Cancer: Long-standing gallstones increase the risk of gallbladder cancer.
In summary, gallstones require careful management. Seek medical attention promptly if you experience symptoms or suspect complications. 🌟
Remember to consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice. 🩺




Comments